DIFFUSION WELDING IN VACUUM
Diffusion welding is a type of pressure welding in which welding is occurred by means of plastic deformation of microroughness on the surface of parts for welding at temperature less that melting temperature.
An outstanding character of this way of welding is in using high temperatures and relative low specific compression pressures.
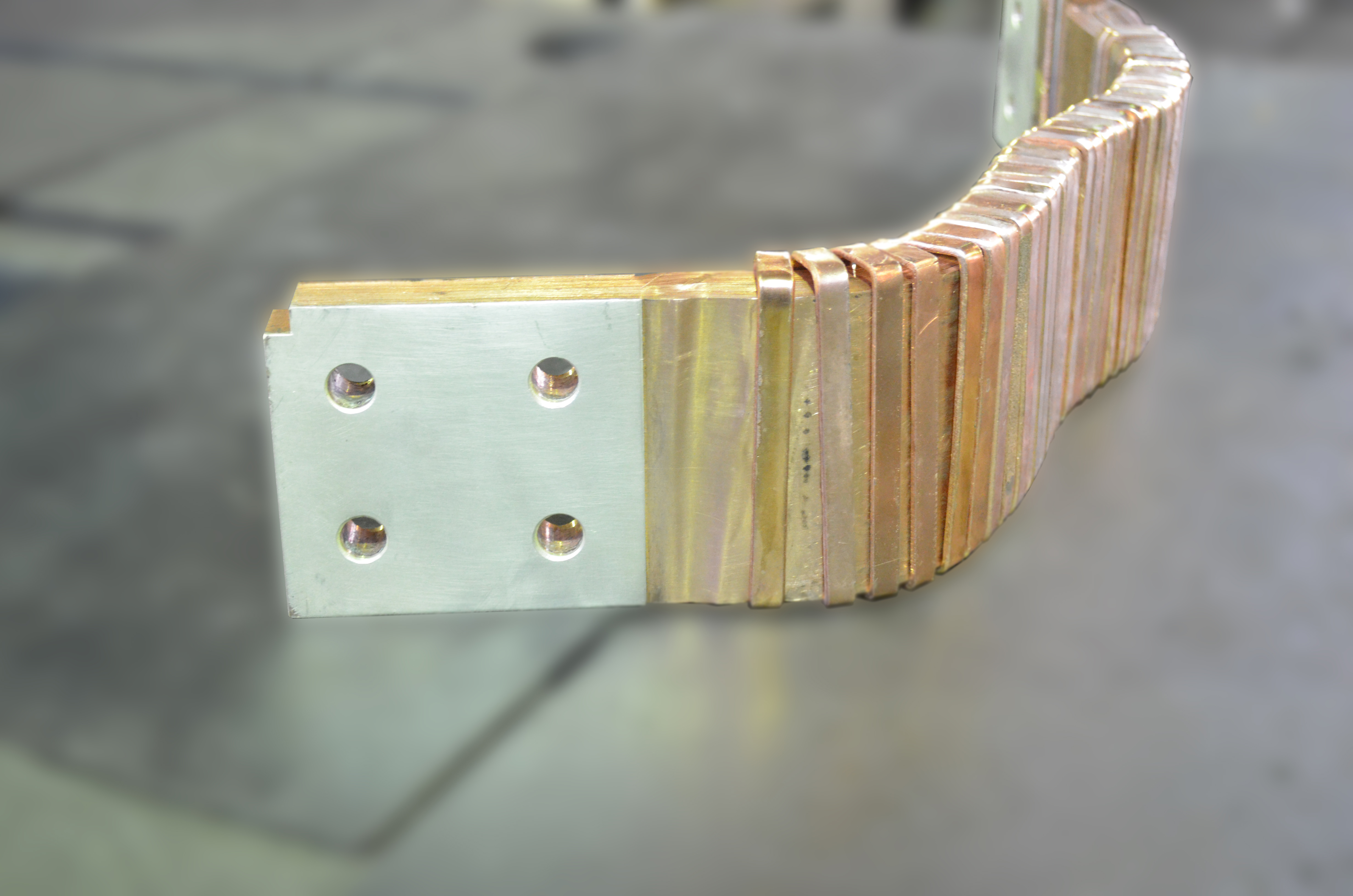
Advantages:
· Possibility of welding joints with minimal deformation less than 5%. Size tolerances of parts manufactured by diffusion welding are comparable with tolerances of parts produced by mechanical machining. This advantage gives possibility to manufacture complex parts by diffusion welding which can not be produced by other methods;
· In joints there are no most part of defects which are common for traditional methods of welding: pinholes, cavities, oxide inclusions. Mechanical characteristics of joints are stable with deviation less than 2...5 %;
· Power consumption of diffusion welding is less than 4-6 times with comparison of flash welding or resistance welding;
· Non-waste technology;
· High quality technology (high strength, corrosion and temperature resistance, aesthetic appearance).
Diffusion welding capability:
· Practically all known construction materials on metal base, ferrite metal, ceramics, glasses, quartz, sapphire, graphite, semiconducting materials in similar and dissimilar combinations;
· Porous, sintered powder metal, composite materials without texture and characteristics brakeage;
· Dissimilar metals and alloys inclined to nesh phase formation, high melting metals (tungsten, niobium, tantalum and etc.);
· Metals with non-metals: steel with graphite, glass with copper and etc.;
The welded parts can be very different by the shape and have compact or developed contact surfaces. Geometry dimensions of welded parts are in limits from several micrometers (semiconducting equipment production) up to several meters (layer-built constructions production).